
How To Tell If You Have Dandruff or Seborrheic Dermatitis?
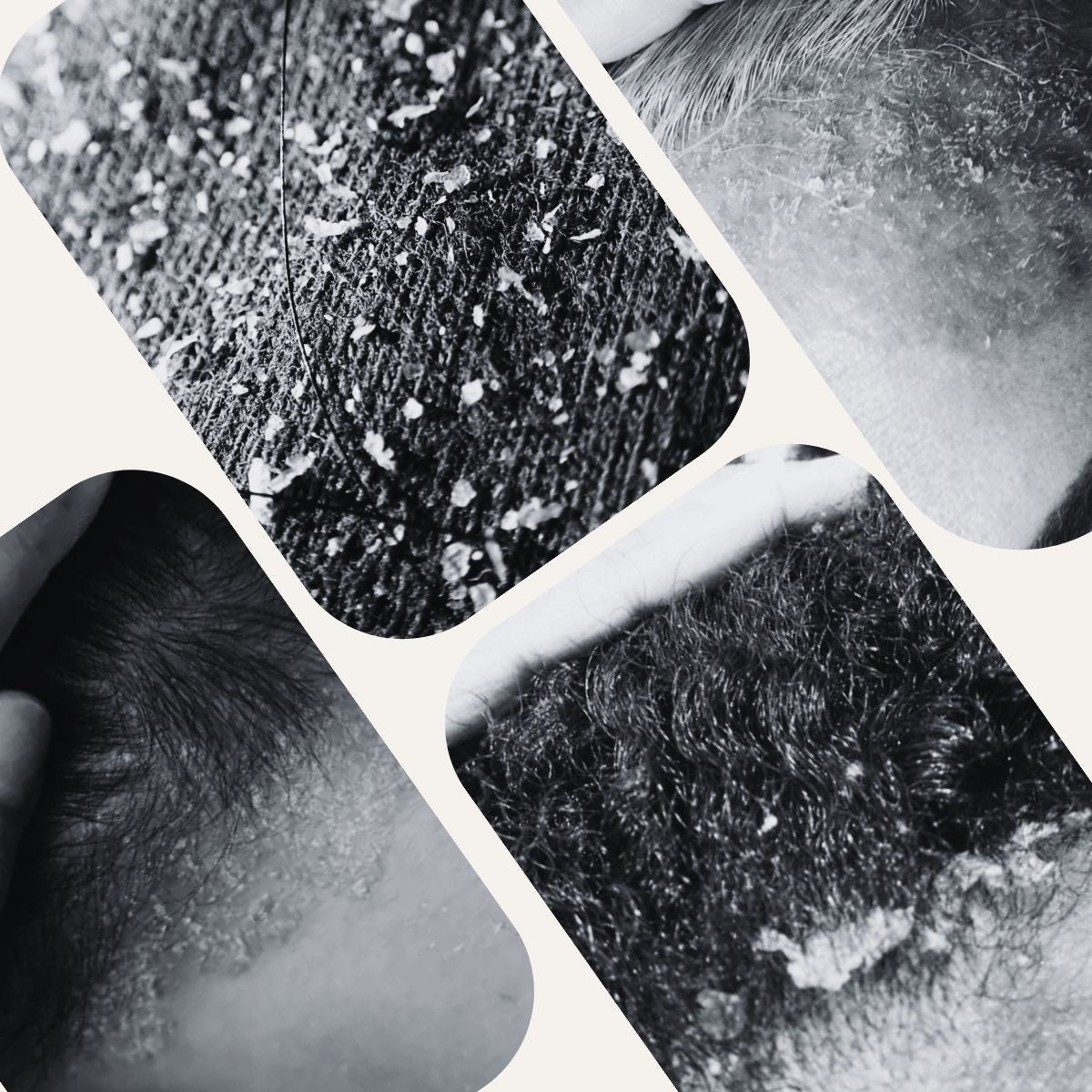
Understanding Seborrhoeic Dermatitis and Dandruff: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment!
Seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff are common skin conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. Though often confused with each other, they differ in severity and symptoms. This article will explore the distinctions between seborrhoeic dermatitis and dandruff, their causes, symptoms, and the best ways to manage and treat them.
What is Dandruff?
Dandruff, known medically as pityriasis capitis, is a mild, chronic scalp condition characterized by the shedding of dead skin cells. It results in white or greyish flakes appearing on the scalp and in the hair. Dandruff is often accompanied by itching and mild irritation, but it does not usually cause significant inflammation.
Causes of Dandruff
The exact cause of dandruff is not fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute:
- Malassezia Yeast: A naturally occurring fungus on the scalp, Malassezia feeds on sebum (the oil produced by sebaceous glands). In some people, this fungus irritates the scalp, leading to an increased turnover of skin cells, which then flake off as dandruff.
- Dry Skin: People with dry skin are more prone to dandruff, especially during winter when indoor heating can exacerbate the dryness.
- Sensitivity to Hair Products: Certain shampoos, conditioners, and styling products can irritate the scalp, leading to dandruff.
- Infrequent Hair Washing: Not washing your hair often enough can lead to an accumulation of oil and skin cells on the scalp, resulting in dandruff.
Symptoms of Dandruff
- White or grey flakes on the scalp and in the hair.
- Itchy scalp.
- Scalp dryness or mild irritation.
What is Seborrhoeic Dermatitis?
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is a more severe and chronic form of skin inflammation that affects not only the scalp but also other oily areas of the body, such as the face, upper chest, and back. It is characterized by red, inflamed skin with greasy, yellowish scales. Unlike dandruff, seborrhoeic dermatitis can cause significant discomfort and may lead to secondary infections if not properly treated.
Causes of Seborrhoeic Dermatitis
The causes of seborrhoeic dermatitis are multifactorial and not entirely understood. However, some key factors include:
- Overgrowth of Malassezia Yeast: Similar to dandruff, Malassezia yeast plays a significant role in seborrhoeic dermatitis, but the reaction is more severe, leading to inflammation and scaling.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of seborrhoeic dermatitis can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Environmental Factors: Cold, dry weather and stress can exacerbate the symptoms.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Individuals with compromised immune systems or certain neurological conditions (e.g., Parkinson's disease) are more prone to seborrhoeic dermatitis.
Symptoms of Seborrhoeic Dermatitis
- Red, inflamed skin covered with greasy, yellowish scales.
- Itching and burning sensation on the affected areas.
- Flaky patches on the scalp, face, eyebrows, chest, and back.
- In severe cases, crusting or thickened skin may develop.
Dandruff vs. Seborrhoeic Dermatitis: Key Differences
- Severity: Dandruff is generally a mild condition, whereas seborrhoeic dermatitis is more severe, involving inflammation and extensive scaling.
- Affected Areas: Dandruff is confined to the scalp, while seborrhoeic dermatitis can affect multiple areas of the body.
- Symptoms: Dandruff primarily causes flaking and itching, while seborrhoeic dermatitis can lead to redness, swelling, and greasy scales.
Treatment and Management
For Dandruff:
- Medicated Shampoos: Over-the-counter shampoos containing zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or salicylic acid can help control dandruff.
- Regular Washing: Frequent washing with a mild shampoo helps reduce oiliness and flakiness.
- Avoid Irritants: Identify and avoid hair care products that irritate your scalp.
For Seborrhoeic Dermatitis:
- Antifungal Treatments: Medicated shampoos or creams containing ketoconazole or ciclopirox are often prescribed to reduce Malassezia yeast overgrowth.
- Anti-inflammatory Creams: Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors may be used to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moisturizers: Non-greasy moisturizers can help soothe dry, irritated skin.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing stress, avoiding harsh weather conditions, and maintaining a balanced diet may help control flare-ups.
While dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis share some similarities, they are distinct conditions that require different approaches to treatment and management. Understanding the symptoms and underlying causes of each can help in choosing the appropriate treatment. For persistent or severe cases, it is always advisable to consult a dermatologist to develop a tailored treatment plan. With the right care, both conditions can be effectively managed, leading to healthier skin and scalp.







Leave a comment